A SQL trigger is a database object which fires when an event occurs in a database. We can execute a SQL query that will “do something” in a database when a change occurs on a database table such as a record is inserted or updated or deleted. For example, a trigger can be set on a record insert in a database table.
Types of Triggers
There are two types of triggers:
- DDL Trigger
- DML Trigger
DDL Triggers
The DDL triggers are fired in response to DDL (Data Definition Language) command events that start with Create, Alter and Drop, such as Create_table, Create_view, drop_table, Drop_view and Alter_table.
Code of a DDL Trigger
create trigger saftey
on database
for
create_table,alter_table,drop_table
as
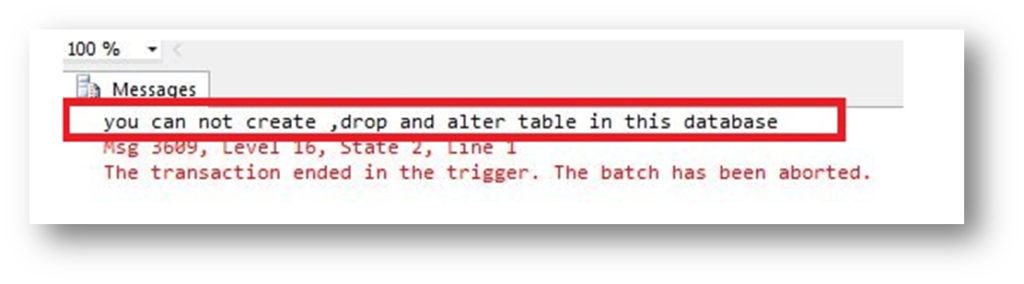
print’you can not create ,drop and alter table in this database’
rollback;
When we create, alter or drop any table in a database then the following message appears:
DML Triggers
The DML triggers are fired in response to DML (Data Manipulation Language) command events that start with Insert, Update, and Delete. Like insert_table, Update_view and Delete_table.
Code of a DML Trigger
create trigger deep
on emp
for
insert,update,delete
as
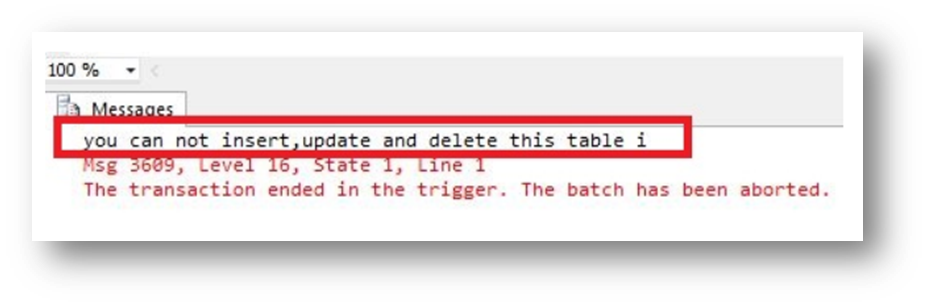
print’you can not insert,update and delete this table i’
rollback;
When we insert, update or delete in a table in a database then the following message appears,
There are two types of DML triggers
AFTER Triggers
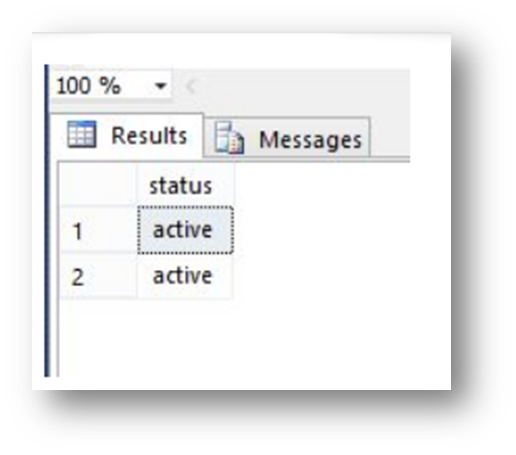
AFTER triggers are executed after the action of an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement.
create trigger insertt
on emp
after insert
as
begin
insert into empstatus values(‘active’)
end
INSTEAD Of Triggers
It will tell the database engine to execute the trigger instead of executing the statement. For example an insert trigger executes when an event occurs instead of the statement that would insert the values in the table .
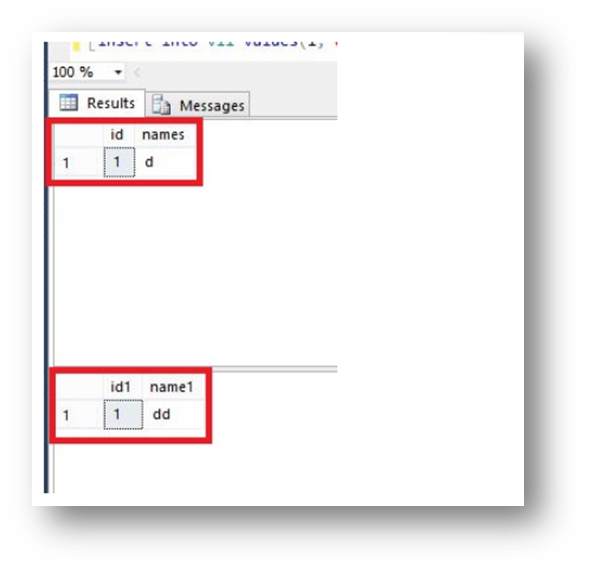
CREATE TRIGGER instoftr
ON v11
INSTEAD OF INSERT
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO emp
SELECT I.id, I.names
FROM INSERTED I
INSERT INTO emp1values
SELECT I.id1, I.name1
FROM INSERTED I
END
When we insert data into a view by the following query then it inserts values in both tables :

You can see both tables by the folowing query: