Introduction to Information System (IS)
Meaning of Information System
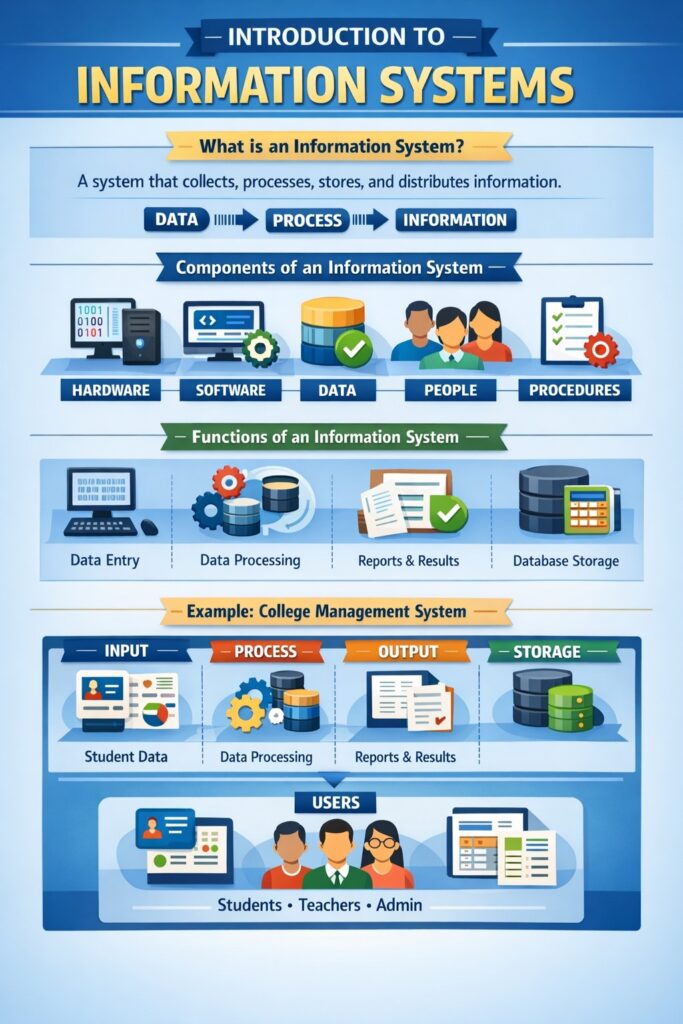
An Information System (IS) is a structured combination of people, hardware, software, data, and procedures that work together to collect, process, store, and distribute information. The main purpose of an information system is to support decision-making, coordination, control, analysis, and visualization in an organization.
In simple words,
👉 Information System = Data + Processing + Useful Information
Difference between Data and Information
- Data: Raw facts and figures without meaning
Example: Marks = 65, 72, 80 - Information: Processed data that is meaningful
Example: Average marks = 72.33 → Student performance is good
Components of an Information System
An information system consists of five major components:
- Hardware
- Physical devices like computers, servers, printers, routers
- Example: Desktop used in college office
- Software
- Programs and applications that run on hardware
- Example: Payroll software, ERP, Student Management System
- Data
- Raw facts stored in databases
- Example: Student records, employee salary data
- People
- Users who operate and manage the system
- Example: Students, teachers, system administrators
- Procedures
- Rules and instructions for using the system
- Example: Steps for login, data entry, backup policy
Basic Functions of an Information System
An information system performs the following key functions:
- Input
- Collecting raw data
- Example: Entering student marks
- Processing
- Converting data into information
- Example: Calculating total and percentage
- Output
- Producing useful information
- Example: Result sheet
- Storage
- Saving data for future use
- Example: Database storage
- Feedback
- Checking output and improving input
- Example: Correcting errors in marks
Types of Information Systems
- Transaction Processing System (TPS)
- Handles day-to-day transactions
- Example: Railway reservation system
- Management Information System (MIS)
- Supports managerial decision-making
- Example: Monthly sales report
- Decision Support System (DSS)
- Helps in complex decision-making
- Example: Business forecasting system
- Executive Information System (EIS)
- Used by top-level management
- Example: Dashboard showing company performance
- Office Automation System (OAS)
- Supports office work
- Example: Email, Word processing
Role of Information System in Organizations
- Improves efficiency and productivity
- Helps in quick and accurate decision-making
- Enhances data security and control
- Reduces manual work and errors
- Supports planning and forecasting
Example of Information System (College Management System)
Scenario
A college uses a College Management Information System (CMIS).
- Input: Student admission details, marks, attendance
- Processing: Result calculation, fee status, attendance percentage
- Output: Mark sheets, fee receipts, attendance reports
- Storage: Student database
- Users: Students, teachers, admin staff
📌 Result: Faster administration, transparency, and accuracy
Importance of Information System in Cyber Security
- Protects confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data
- Helps in access control and authentication
- Supports audit trails and monitoring
- Essential for legal compliance under Cyber Laws
Conclusion
An Information System is the backbone of modern organizations. It transforms raw data into meaningful information, enabling organizations to work efficiently, securely, and legally. In the field of Information Security and Cyber Law, understanding information systems is crucial to protect digital assets and comply with legal requirements.
