Computer Security Concepts
Introduction
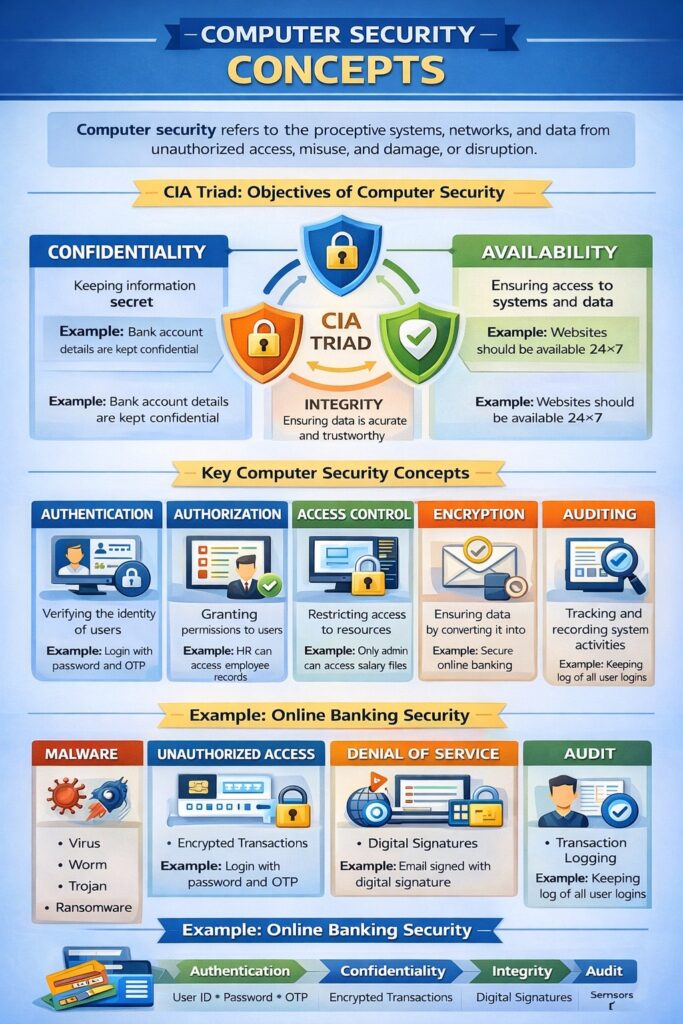
Computer Security refers to the protection of computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, misuse, damage, or disruption. It ensures that information and computing resources are used safely, correctly, and legally. In Information Security and Cyber Law, computer security forms the foundation of data protection and cyber crime prevention.
Objectives of Computer Security (CIA Triad)
The core concepts of computer security are based on the CIA Triad:
1. Confidentiality
Confidentiality ensures that information is accessible only to authorized users.
Techniques to achieve confidentiality:
- User authentication (ID & password)
- Encryption
- Access control policies
- Firewalls
Example:
Only authorized bank employees can access customer account details.
2. Integrity
Integrity ensures that data is accurate, complete, and not altered without authorization.
Techniques to maintain integrity:
- Hash functions
- Digital signatures
- Checksums
- Audit logs
Example:
Marks stored in a university database should not be modified illegally.
3. Availability
Availability ensures that information and systems are accessible when needed.
Techniques to ensure availability:
- Backup and recovery
- Fault tolerance
- Redundant systems
- Protection against DoS attacks
Example:
ATM services should be available 24×7.
Key Computer Security Concepts
1. Authentication
Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a user or system.
Types of authentication:
- Something you know → Password, PIN
- Something you have → Smart card, OTP
- Something you are → Fingerprint, face recognition
Example:
Logging into email using password and OTP.
2. Authorization
Authorization determines what actions an authenticated user is allowed to perform.
Example:
- Student → View results
- Admin → Modify results
📌 Authentication comes before authorization.
3. Access Control
Access control defines rules and mechanisms to restrict access to resources.
Models of Access Control:
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Example:
Only HR department can access salary files.
4. Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting plain text into cipher text to protect data.
Types:
- Symmetric encryption (AES, DES)
- Asymmetric encryption (RSA)
Example:
HTTPS encrypts data between browser and server.
5. Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation ensures that a sender cannot deny sending a message.
Techniques used:
- Digital signatures
- Time stamps
Example:
Online contract signed using digital signature.
6. Auditing and Accountability
Auditing involves tracking and recording system activities to detect misuse.
Example:
- Login logs
- Transaction logs
📌 Helps in cyber crime investigation and legal evidence.
Threats to Computer Security
1. Malware
- Virus
- Worm
- Trojan horse
- Ransomware
- Spyware
2. Unauthorized Access
- Hacking
- Password cracking
3. Denial of Service (DoS)
- Overloading system to make it unavailable
4. Insider Threats
- Employees misusing access rights
Security Mechanisms
| Mechanism | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Firewall | Network protection |
| Antivirus | Malware detection |
| IDS/IPS | Intrusion detection |
| Backup | Data recovery |
| Patch management | Fix vulnerabilities |
Computer Security and Cyber Law (Indian Context)
Computer security is legally supported by:
- IT Act, 2000
- Section 43 → Damage to computer systems
- Section 65 → Tampering with computer source code
- Section 66 → Computer-related offences
📌 Poor security can lead to legal liability.
Example: Computer Security in Online Banking System
- Authentication → User ID + Password + OTP
- Confidentiality → Encrypted transactions
- Integrity → Digital signatures
- Availability → 24×7 servers with backup
- Audit → Transaction logs
Advantages of Computer Security
- Protects sensitive data
- Prevents cyber crimes
- Ensures business continuity
- Builds user trust
- Supports legal compliance
Conclusion
Computer security is essential to protect digital assets from growing cyber threats. Concepts like CIA triad, authentication, encryption, access control, and auditing form the backbone of secure systems. In today’s digital world, strong computer security is not only a technical requirement but also a legal and ethical necessity.
