Classification and Components of Information System
1. Classification of Information System
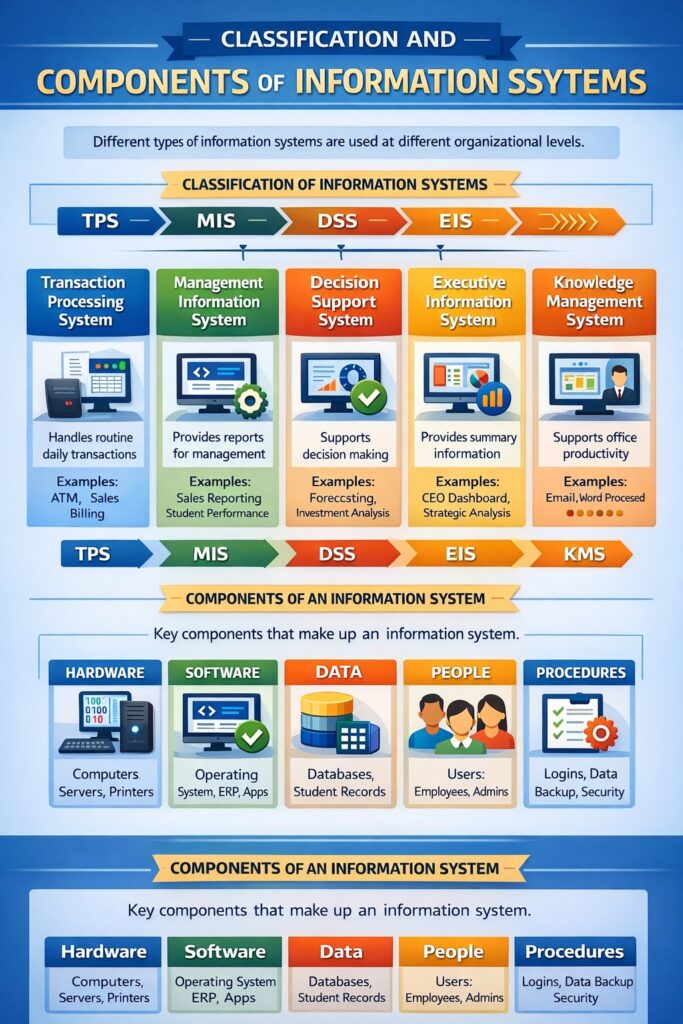
Information Systems can be classified on the basis of organizational level and purpose. This classification is very important from MCA exam point of view.
1. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
Definition:
TPS is an information system that handles routine, day-to-day business transactions accurately and efficiently.
Features:
- High volume of data
- Repetitive operations
- Real-time or batch processing
Examples:
- ATM transactions
- Railway reservation system
- Sales billing system
Users: Clerical staff, operators
2. Management Information System (MIS)
Definition:
MIS provides summarized reports to middle-level management for planning and control.
Features:
- Uses data from TPS
- Periodic reports (weekly, monthly)
- Structured decisions
Examples:
- Monthly sales report
- Student performance report
Users: Managers, department heads
3. Decision Support System (DSS)
Definition:
DSS supports semi-structured and unstructured decision-making using analytical models and data.
Features:
- What-if analysis
- Forecasting
- Interactive system
Examples:
- Business forecasting system
- Investment decision system
Users: Senior managers, analysts
4. Executive Information System (EIS) / Executive Support System (ESS)
Definition:
EIS provides high-level summarized information to top management.
Features:
- Graphical dashboards
- Key performance indicators (KPIs)
- External and internal data
Examples:
- CEO dashboard
- Company growth analysis system
Users: Top executives
5. Office Automation System (OAS)
Definition:
OAS supports office-related activities and improves productivity.
Examples:
- Email systems
- Word processing
- Video conferencing
Users: Office staff, executives
6. Knowledge Management System (KMS)
Definition:
KMS captures, stores, and shares organizational knowledge.
Examples:
- E-learning platforms
- Corporate knowledge portals
Users: Employees, trainers
Diagram (Exam-friendly text format)
TPS → MIS → DSS → EIS
(Operational → Managerial → Strategic level)
2. Components of Information System
An Information System consists of five essential components:
1. Hardware
Definition:
Physical devices used in the system.
Examples:
- Computers, servers
- Routers, printers
- Storage devices
2. Software
Definition:
Programs that control hardware and process data.
Types:
- System software (OS)
- Application software (ERP, MIS)
Examples:
- Windows, Linux
- Payroll software
3. Data
Definition:
Raw facts stored in databases.
Examples:
- Student records
- Employee salary data
📌 Data is the most valuable asset in an Information System.
4. People
Definition:
Users who interact with the system.
Examples:
- End users
- System analysts
- Database administrators
5. Procedures
Definition:
Rules and instructions for operating the system.
Examples:
- Login process
- Data backup policy
- Security guidelines
Components Linked with Information Security
From Information Security perspective, components must ensure:
- Confidentiality → Access control, encryption
- Integrity → Validation, audit trails
- Availability → Backup, disaster recovery
Comparison Table (Quick Revision)
| Classification | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| TPS | Daily transactions | ATM |
| MIS | Managerial reports | Monthly sales |
| DSS | Decision making | Forecasting |
| EIS | Strategic decisions | CEO dashboard |
| OAS | Office work | |
| KMS | Knowledge sharing | E-learning |
Conclusion
Information Systems are classified based on organizational needs and decision levels, while their components work together to transform data into useful information. Understanding both classification and components is essential for designing secure and legally compliant information systems.
