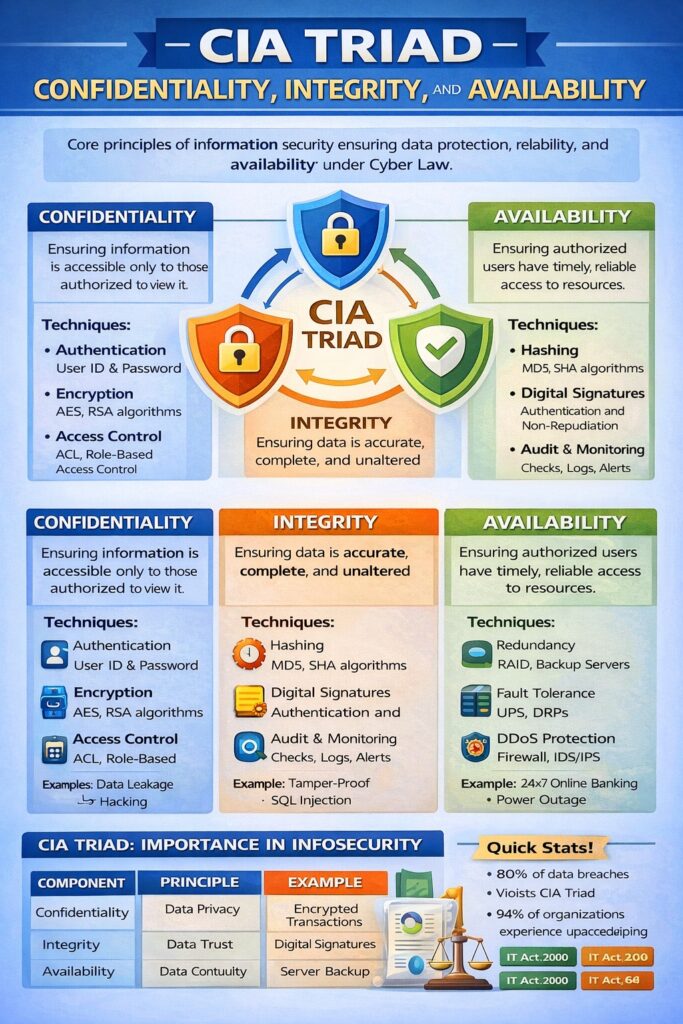
CIA Triad (Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability)
Introduction
The CIA Triad is the foundation of Information Security and Computer Security. It represents three core objectives that every secure information system must achieve:
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
These principles guide the design, implementation, and evaluation of security policies, controls, and technologies. Any violation of CIA can lead to data breaches, cyber crimes, financial loss, and legal consequences under Cyber Law.
1. Confidentiality
Meaning
Confidentiality ensures that information is accessible only to authorized persons and is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals, systems, or processes.
📌 “Information should be kept secret from unauthorized users.”
Why Confidentiality is Important
- Protects sensitive data (personal, financial, business)
- Prevents identity theft and fraud
- Maintains trust of users and customers
- Ensures legal compliance (IT Act, GDPR, etc.)
Techniques to Achieve Confidentiality
- Authentication
- User ID & Password
- OTP, Biometrics
- Access Control
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Least privilege principle
- Encryption
- Symmetric encryption (AES)
- Asymmetric encryption (RSA)
- Network Security
- Firewalls
- VPN
- Data Masking & Tokenization
Examples
- Bank account details accessible only to account holder
- Student results visible only to authorized students
- Encrypted WhatsApp messages
Violation of Confidentiality
- Data leakage
- Eavesdropping
- Hacking
- Phishing attacks
2. Integrity
Meaning
Integrity ensures that data is accurate, complete, and has not been altered without authorization.
📌 “Information should not be modified illegally or accidentally.”
Why Integrity is Important
- Ensures correctness of information
- Prevents fraud and manipulation
- Essential for decision-making
- Maintains data reliability
Techniques to Maintain Integrity
- Hash Functions
- MD5, SHA algorithms
- Digital Signatures
- Ensures data authenticity and integrity
- Checksums
- Error detection in data transmission
- Audit Trails
- Logs of changes made to data
- Version Control & Backups
Examples
- Marks in a university database should not be changed illegally
- Online transaction amount must not be altered
- Software source code protected from tampering
Violation of Integrity
- Data tampering
- SQL injection attacks
- Malware modifying files
- Insider attacks
3. Availability
Meaning
Availability ensures that information and systems are accessible to authorized users whenever required.
📌 “Information should be available on time.”
Why Availability is Important
- Supports business continuity
- Prevents service disruption
- Ensures user satisfaction
- Critical for real-time systems (banking, healthcare)
Techniques to Ensure Availability
- Backup and Recovery
- Regular data backups
- Disaster recovery plans
- Redundancy
- Backup servers
- Load balancing
- Fault Tolerance
- RAID
- Failover systems
- Protection Against Attacks
- DoS / DDoS protection
- IDS/IPS systems
Examples
- ATM services available 24×7
- E-commerce websites accessible during sales
- Hospital systems always operational
Violation of Availability
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
- Hardware failure
- Power outages
- Ransomware attacks
CIA Triad – Combined View
| Aspect | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Prevent unauthorized access | Encrypted bank data |
| Integrity | Prevent unauthorized modification | Digital signatures |
| Availability | Ensure continuous access | 24×7 online services |
📌 All three are interdependent—weakness in one affects the others.
CIA Triad and Cyber Law (Indian Context)
- IT Act, 2000
- Section 43 → Damage to data and systems
- Section 65 → Tampering with computer source code
- Section 66 → Computer-related offences
Failure to maintain CIA can result in legal penalties and compensation.
Real-Life Example: Online Banking System
- Confidentiality → Encrypted transactions, secure login
- Integrity → Digital signatures, transaction validation
- Availability → 24×7 servers, backups, disaster recovery
Advantages of CIA Model
- Simple and effective security framework
- Helps in risk assessment
- Supports policy making
- Widely accepted globally
Conclusion
The CIA Triad is the cornerstone of information security. Confidentiality protects data from unauthorized access, integrity ensures correctness and trustworthiness, and availability guarantees uninterrupted access. A secure system must balance all three to protect information assets effectively and legally.
