“A procedures or function is a group or set of SQL and PL/SQL statements that perform a specific task.”
A function and procedure is a named PL/SQL Block which is similar . The major difference between a procedure and a function is, a function must always return a value, but a procedure may or may not return a value.
Procedures
A procudure is a named PL/SQL block which performs one or more specific task. This is similar to a procedure in other programming languages. A procedure has a header and a body.
The header consists of the name of the procedure and the parameters or variables passed to the procedure.
The body consists or declaration section, execution section and exception section similar to a general PL/SQL Block.
A procedure is similar to an anonymous PL/SQL Block but it is named for repeated usage.
We can pass parameters to procedures in three ways :
| Parameters | Description |
| IN type | These types of parameters are used to send values to stored procedures. |
| OUT type | These types of parameters are used to get values from stored procedures. This is similar to a return type in functions. |
| IN OUT type | These types of parameters are used to send values and get values from stored procedures. |
A procedure may or may not return any value.
Syntax:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] PROCEDURE procedure_name (<Argument> {IN,
OUT, IN OUT} <Datatype>,…) IS Declaration section<variable,constant> ; BEGIN Execution section EXCEPTION Exception section END
Example
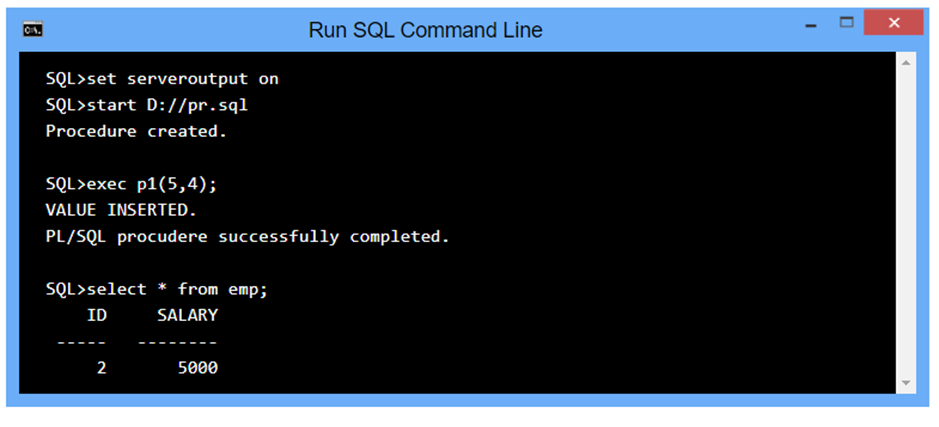
create table named emp have two column id and salary with number datatype.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE p1(id IN NUMBER, sal IN NUMBER) AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO emp VALUES(id, sal); DBMD_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(‘VALUE INSERTED.’);
END;
/
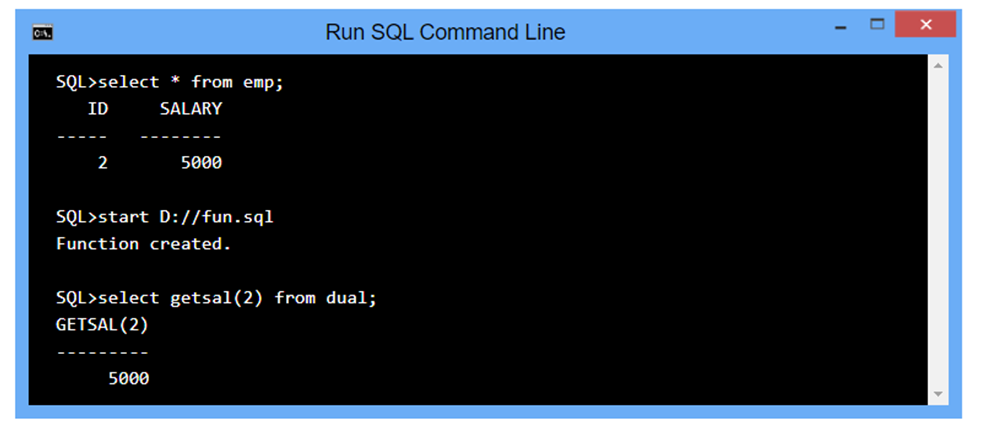
OUTPUT
Functions
A function is a named PL/SQL Block which is similar to a procedure. The major difference between a procedure and a function is, a function must always return a value, but a procedure may or may not return a value.
Syntax:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name [parameters]
RETURN return_datatype; {IS, AS}
Declaration_section <variable,constant> ;
BEGIN Execution_section Return return_variable;
EXCEPTION exception section Return return_variable;
END;
RETURN TYPE: The header section defines the return type of the function. The return datatype can be any of the oracle datatype like varchar, number etc.
The execution and exception section both should return a value which is of the datatype defined in the header section.
How to execute a Function?
A function can be executed in the following ways.
- As a part of a SELECT statement : SELECT emp_details_func FROM dual;
- In a PL/SQL Statements like, : dbms_output.put_line(emp_details_func);
This line displays the value returned by the function .
Example
create or replace function getsal (no IN number) return number
is
sal number(5);
begin
select salary into sal from emp where id=no;
return sal;
end;
/
Output